Good morning, it’s Monday. In case you blinked, here’s what you missed: OpenAI’s o3-Mini is here—faster, smarter, and ready to flex—while Microsoft’s new AI think tank is busy predicting humanity’s future. The EU just slammed the door on ‘risky’ AI, Intel secured billions in CHIPS Act funding, and Trump is cozying up to NVIDIA’s CEO over AI and China concerns.
And in our latest Forward Future Original article, we break down why o3-Mini—a small yet mighty model—marks a turning point in AI development.
🗞️ ICYMI RECAP
Top Stories You Might Have Missed
🔥 OpenAI o3-Mini: Faster, Smarter, and Cheaper AI
OpenAI's o3-mini is a next-gen small reasoning model optimized for STEM, coding, and logic, offering improved accuracy and 24% faster responses than its predecessor. It introduces function calling, structured outputs, and reasoning adjustments for greater flexibility. Available now for ChatGPT Plus, Team, and Pro users, with Enterprise access coming soon. Free users can test it via the "Reason" option in ChatGPT.
🏙️ Microsoft’s New AI Unit Tackles Societal Impact
Microsoft's Advanced Planning Unit (APU) will research AI’s long-term effects on society, health, and work. Led by Microsoft AI CEO Mustafa Suleyman, it will provide insights, product recommendations, and reports. The company is hiring experts across various fields to contribute. This initiative aligns with Microsoft’s AI-focused strategy and industry-wide efforts, including OpenAI’s recent appointment of a chief economist to study AI’s economic impact.
🙅 EU Enforces Ban on 'Unacceptably Risky' AI Systems
As of February 2, 2025, the European Union has enacted a ban on artificial intelligence systems deemed to pose "unacceptable risks" to safety or fundamental rights. This move, part of the EU's comprehensive AI Act, targets applications such as social scoring, real-time biometric surveillance in public spaces, and AI tools that manipulate human behavior. The legislation categorizes AI into risk levels—unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal—imposing stricter regulations on higher-risk applications.
💰 Intel Lands $2.2B in CHIPS Act Grants
Intel has received $2.2 billion in federal grants from the U.S. CHIPS and Science Act, with $5.66 billion still to come. The funds, part of a $7.86 billion total award, support semiconductor manufacturing and packaging in Arizona, New Mexico, Ohio, and Oregon. Despite uncertainty under the Trump administration, Intel remains optimistic, citing positive discussions with federal officials. The CHIPS Act, signed in 2022, aims to boost domestic chip production with $52 billion in subsidies.
🤝 Trump & NVIDIA CEO Discuss AI, China Risks
Donald Trump will meet NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang amid rising concerns over China's AI advancements, particularly DeepSeek’s market impact. While planned earlier, the meeting now underscores NVIDIA’s opposition to Biden’s stricter export controls on AI chips. Trump sees AI as an economic opportunity, while lawmakers push for tighter restrictions. Notably, Tesla CEO Elon Musk, a frequent Trump advisor, is not expected to attend.
🕶️ Zuckerberg Pushes AI Glasses Amid Rising Internal Tensions
Mark Zuckerberg believes AI-powered AR glasses could be a multi-billion-dollar market, calling 2025 a pivotal year. Ray-Ban Meta glasses exceeded sales targets, but Reality Labs lost $5 billion last quarter despite a 40% revenue boost. Internal tensions are rising over Zuckerberg’s ties to Trump and DEI policies. Meanwhile, Meta is investing $65 billion in AI infrastructure while planning layoffs for so-called “low-performers.”
⚖️ AI Startup Perplexity Faces Trademark Lawsuit
AI search startup Perplexity is being sued by Texas-based Perplexity Solved Solutions for trademark infringement. The lawsuit, filed in California, claims Perplexity ignored a cease and desist letter and refused to buy the trademark, which covers HR and collaboration tools. Meanwhile, Perplexity also faces a separate lawsuit from News Corp over content scraping. The Texas firm seeks damages, a name ban, and domain transfers.
🏗️ Blackstone Stays Bullish on AI Data Centers
Despite DeepSeek’s AI efficiency gains, Blackstone sees continued demand for data centers. President Jonathan Gray reassured investors that AI usage will keep rising, requiring more infrastructure. Blackstone has invested heavily, including a $10 billion QTS acquisition and a $16 billion AirTrunk deal. While its stock rose 40% in a year, it dipped 3% post-DeepSeek. The firm aims to dominate AI infrastructure investment globally.
🚫 Italy Bans DeepSeek AI Over Privacy Risks
Italy’s data watchdog has blocked DeepSeek AI, citing transparency failures and noncompliance with European privacy laws. Regulators launched an investigation after the Chinese firm denied operating in Italy while allegedly collecting user data. DeepSeek also faces security concerns, including jailbreak exploits and unauthorized use of OpenAI data. The ban follows Italy’s temporary ChatGPT block in 2023, highlighting Europe’s growing scrutiny of AI regulation.
©️ AI-Written Book Stirs Copyright Concerns
BBC’s Zoe Kleinman was surprised by an AI-generated book in her name, made in minutes by BookByAnyone. While meant as a novelty, it highlights growing fears about AI using copyrighted work without consent. Critics warn this threatens creative industries, while ongoing lawsuits and Trump’s repeal of Biden’s AI regulations add to legal uncertainty. The case underscores the urgent debate over AI and intellectual property rights.
☝️ POWERED BY RENDERNET.AI
Revolutionize Your Music Videos with AI!
Discover how RenderNet.ai brings your vision to life with stunning character consistency, ensuring your stars shine the same in every frame. Dive into the future of creative storytelling—watch the AI magic in action today! 🎬
👾 FORWARD FUTURE ORIGINAL
Small, Fast, and Powerful: How o3-Mini Redefines AI Efficiency and Performance
OpenAI has released o3-mini, a model that was announced in December and is now available in two versions: ‘Low’ and ‘High.’ The ‘High’ variant is only slightly more expensive than o1-Small but clearly outperforms Full-o1 in most benchmarks. This marks a turning point—one we’ll remember as the start of a new chapter. In this article, I will explain why the release of o3 and o3-mini is a milestone in AI history
What makes o3-mini so important?
o3-mini is a smaller language model, but it offers such strong performance that it outperforms even OpenAI's best reasoning model to date, full o1 on most benchmarks (with the exception of o1-Pro). But not only the performance is remarkable - the costs are too. In the Codeforce benchmark, o3-mini achieves almost 200 points more Elo than o1, at almost the same cost as o1-mini. That is breathtaking.
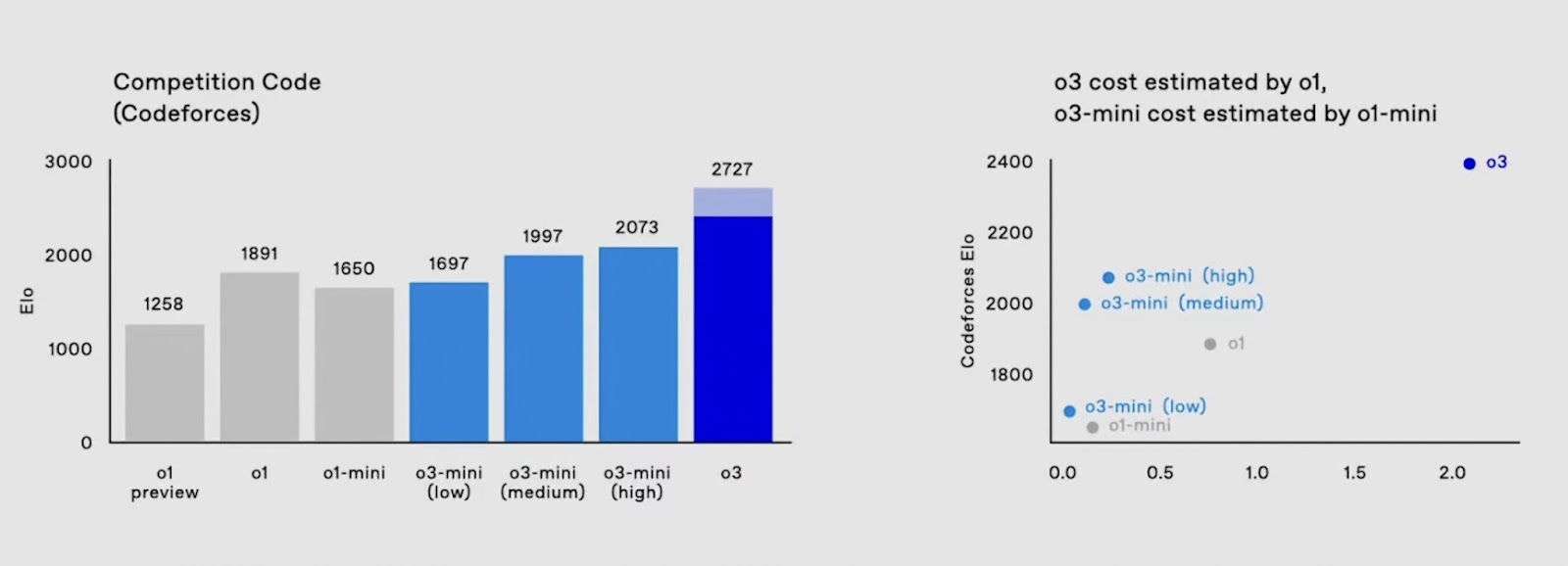
The development of o3 allows several conclusions to be drawn: we are not only seeing regular improvements to the models, but also a reduction in their size and cost. Some joke that AGI will one day run on a smart fridge. Given current trends, that idea is no longer far-fetched. We are increasingly seeing small language models that are significantly more powerful than state-of-the-art LLMs just a few months ago - and so efficient that they can be operated “on the edge” without any problems. Models with 1.5 billion parameters that run on a smartphone and are sufficient for everyday use. This is exactly where o3-mini comes in: It shows how good small (reasoning) models have become and how rapidly development is progressing. → Continue reading here.
🏠 INDOOR TRAINING
Training AI in Controlled Environments May Improve Performance in Uncertain Ones
The Recap: MIT researchers have discovered an unexpected twist in AI training: sometimes, training AI agents in a simpler, noise-free environment leads to better performance in unpredictable, real-world conditions. This counterintuitive finding, dubbed the indoor training effect, suggests that less environmental randomness during training can result in more adaptable AI agents.
Researchers tested AI agents on modified versions of Atari games, adding varying levels of randomness to game mechanics.
AI agents trained in simpler, noise-free environments performed better in unpredictable settings than those trained with noise from the start.
This challenges the conventional belief that training conditions should closely match deployment environments.
The study focused on reinforcement learning, where AI agents learn through trial and error to maximize rewards.
The key factor seems to be how AI explores its environment: noise-free training helps establish clearer rules before introducing unpredictability.
The effect persisted even when more realistic variations of noise were introduced, reinforcing its significance.
Researchers plan to explore its applications in more complex AI tasks like computer vision and natural language processing.
Forward Future Takeaways:
This discovery could change how AI models are trained, particularly for applications in robotics, autonomous systems, and uncertain real-world environments. Instead of striving for hyper-realistic simulations, researchers and engineers might benefit from intentionally simplifying training conditions to improve generalization. Future work will likely explore how to optimize this approach for broader AI applications. → Read the full article here.
🧪 RESEARCH
Generative AI Enables Rapid Prediction of 3D Genomic Structures
MIT chemists have developed a generative AI model that predicts the three-dimensional structures of genomes from DNA sequences within minutes, significantly accelerating the study of how genomic organization influences gene expression. This breakthrough is crucial because 3D genome structures play a key role in regulating genes, impacting everything from disease development to potential treatments. Traditional methods to determine these structures are slow and expensive, but AI-driven models could democratize access to this data, making advanced genomic research more efficient and widespread.
Researchers hope this approach will lead to new discoveries in cancer research, regenerative medicine, and personalized treatments by providing faster insights into how genes are controlled within cells. Ultimately, this innovation could transform the way scientists understand and manipulate the fundamental mechanics of life itself. → Continue reading here.







Reply